If you’re just starting to learn about the world of big data, it’s easy to get lost in all the jargon. One of the most common misconceptions is the difference between the terms “data mining” and “machine learning.” Both are often used interchangeably. But in fact, they are two different (albeit related) fields.
If you want to work with data in any capacity, then it’s essential that you understand the differences between the two. That’s why we’ve written this guide. Below, we’ll tell you all about the difference between data mining and machine learning, and how both are employed.
Is There a Difference Between Data Mining and Machine Learning?
Yes. Data mining is part of the data analysis process, whereas machine learning is an entire field of study. Broadly speaking, data mining is the process of extracting information from a dataset, whereas machine learning is the process of “teaching” computers how to predict more accurate outcomes.
Data Mining vs. Machine Learning: Discipline
Let’s start our deep dive by taking a look at what data mining and machine learning are in a broad sense.
What Is Data Mining?

Data mining is a pretty self-explanatory term. It’s the process by which you mine useful data from vast reserves of disorganized and largely useless data.
The data that you mine using various mining methods can be subjected to data analysis techniques to reveal hidden patterns. The mining process is thus the first step in using data to produce business intelligence and help make strong business decisions.
What Is Machine Learning?
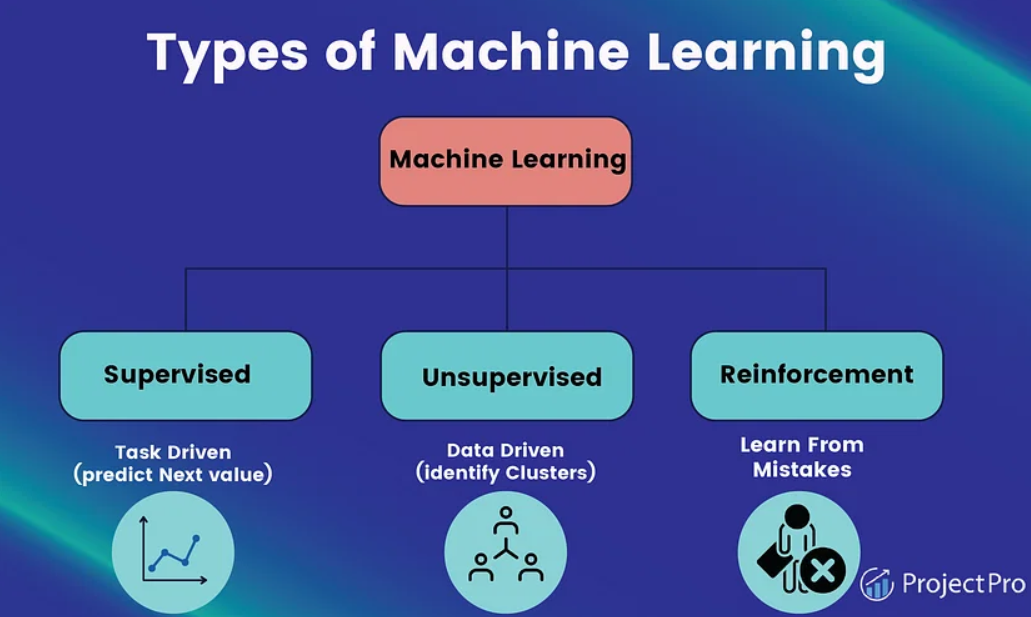
Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on training computers to learn from data so that they can derive their own insights with very little human intervention.
The goal of machine learning is to take what used to be a manual process and turn it into an automated process. Earlier, programmers had to explicitly tell computers what to do at each step of a program. With the emergence of machine learning systems, we can put computers through a training process and have them independently conduct pattern analysis and other tasks.
Data Mining vs. Machine Learning: How Do They Work?
Here’s how machine learning and data mining are each deployed:
How Does Data Mining Work?
The data mining process begins by taking stock of the business objectives of the project. Let’s say that you have a product that can produce a medical diagnosis based on scans provided by a patient. Now you need high-quality data on which you can test this product to determine how accurate it is.
A data analyst working on this project would then proceed to identify sources for the medical scan images. They would choose sources (such as open-access medical repositories) and use techniques like classification and clustering to sift through massive volumes of data to get the exact kind of data required for this project.
The data that you obtain from this step isn’t always ready for modeling or analysis. So the analyst would then proceed to clean the data and structure it so that the analysis process returns accurate results.
How Does Machine Learning Work?
Let’s return to our example of making a medical diagnosis by analyzing scans provided by a patient. A medical professional could label the images based on the appropriate diagnosis, each serving as a training example for a computer. As the medical professional labels each image, the model would slowly learn how they’re being classified, with the ultimate goal of being able to make diagnoses on its own.
The process of building models for machine learning applications is an iterative one. The process starts with an input source of data and an analysis of how well the model absorbs information from training sets. You could then go back to training machine learning models based on the model’s ability to make accurate predictions.
Data Mining vs. Machine Learning: Applications

Both data mining and machine learning have been around long enough that they’re widely used in all kinds of software applications. Let’s take a look at the specific use cases that they’re commonly used for.
What Are the Different Applications of Data Mining?
Let’s take a look at how different sectors used data mining.
Retail
Retailers regularly use data mining to sift through the huge volumes of customer and product data available to them. Supermarkets, for example, can use the technique to determine which SKUs perform the best or to identify what kinds of discounts are most favored by customers during the holiday season.
Agriculture
With IoT and sensors becoming widely used in farming, data mining has had a bigger say in agricultural decision-making. It is used to gather and analyze data pertaining to crop yield, soil quality, weather conditions, and so on.
Insurance
The insurance industry has always used number crunching to make a lot of decisions. Data mining is widely used in this space to guide decision-making pertaining to matching customers with insurance products, detecting fraud, and identifying risky customers.
Marketing
Marketers have access to troves of data each day from various sources. Professionals in this industry regularly use data mining to make large volumes of data more manageable. The insights gained from that process are used to design more efficient marketing campaigns and reduce the cost of acquiring new customers.
What Are the Different Applications of Machine Learning?
Here are a few sectors in which machine learning is prominent.
Image Recognition
Google’s reverse image search and Facebook’s ability to identify your friends in pictures are both examples of how machine learning can be used to identify elements within images and cross-reference them with other images. These are now also used in generative cases where new images of a certain kind need to be reproduced.
Natural Language Processing
Personal assistants like Siri and Alexa are possible only because of developments in the machine learning field. The speech recognition and signal processing carried out by our devices is underpinned by complex machine learning systems.
Self-Driving Cars
A self-driving car is essentially an agglomeration of machine learning systems that use image recognition, natural language processing, and various other techniques to make autonomous driving possible. The neural information processing systems that guide these vehicles are constructed using various different machine learning algorithms.
Related Read: Top 10 Machine Learning Applications
Data Mining vs. Machine Learning: Tools
Both data mining and machine learning software are, of course, built using programming languages to guide their functioning. That said, there are also various tools that are used to streamline workflows and build templates. Let’s take a look at what they are.
Popular Data Mining Tools

Oracle Data Miner
This is an extension that is offered within Oracle’s SQL development product. It provides an easy interface using which you can access features that make it possible to unearth hidden patterns, build relationships between disparate data items, and produce background knowledge to understand a dataset.
IBM SPSS Modeler
The SPSS Modeler is IBM’s attempt at making data mining accessible even to users who may not have a full technical understanding of the process. It has a drag-and-drop editor which you can use to stack different features and carry out mining and analysis on datasets. The visual approach is complemented by the ability to program features using Python and R.
SAS Enterprise Miner
The SAS Enterprise Miner has the ability to mine vast repositories of data and does so in a surprisingly efficient fashion. It also makes it possible to use multiple models on the same dataset and compare their results side-by-side so you can decide which one you want to use going forward in the process.
Popular Machine Learning Tools

IBM Watson
IBM Watson took the world by storm when it first came out thanks to its incredible computational capabilities. Watson Studio makes it simple for developers to access Watson’s capabilities to build machine learning applications. Popular machine learning frameworks like PyTorch, SciKit, and TensorFlow are all accessible via Watson.
Amazon SageMaker
Amazon’s machine-learning product is known as SageMaker. It makes it extremely simple to deploy and maintain machine learning models dealing with large-scale applications. A big advantage of using the product is that it offers an IDE for users with technical skills and a no-code environment for those who aren’t from a technical background.
Apache Mahout
Apache Mahout is a machine learning tool that’s widely used especially by mathematicians and statisticians. This is the case because the product offers features like a distributed linear algebra framework, making it simple to carry out complex operations at scale. Apache Spark is recommended as the backend for Mahout. They’re easy to combine since they both belong to the Apache stable.
Here is a list of some of the most commonly used open-sourced machine learning tools.
Get To Know Other Data Science Students
Meghan Thomason
Data Scientist at Spin
Corey Wade
Founder And Director at Berkeley Coding Academy
Jonathan King
Sr. Healthcare Analyst at IBM
Data Mining vs. Machine Learning: Careers
Data mining and machine learning are both skills that are quite in demand in the software industry. Let’s find out what kind of roles you can land with them.
What Jobs Are Available in Data Mining?
Data professionals who want to focus exclusively on the mining aspect of the field can find work as data mining specialists. These are software professionals who are experts at mining data from various sources and making them easily available for the analysis process.
You can also work in other capacities in the data field if you’re somebody who’s good at data mining. That includes roles such as data analyst, data scientist, and data architect. Although mining isn’t the only thing you’ll be doing at those jobs, being good at mining can help you execute your other tasks more efficiently.
What Jobs Are Available in Machine Learning?
The most common job in this field is that of a machine learning engineer. This is a role where you focus on developing machine learning algorithms and building models for specific use cases.
The other jobs that you can get in machine learning depend on your interests. Engineers who are interested in robotics, for example, can work as robotics engineers. Machine learning developers also often go into areas like natural language processing, cybersecurity, and AI.
Data Mining vs. Machine Learning: Future Outlook
Let’s find out what the prospects are like for a career in machine learning or data mining.
What Does the Future of Data Mining Look Like?
Data mining is a core skill in the field of data science. It’s regularly used by data analysts, data scientists, and data engineers.
The future of all those jobs is bright. According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment for data scientists is going to rise by an incredible 36% between 2021 and 2031. That’s a lot higher than the average for all jobs.
What Does the Future of Machine Learning Look Like?
The field of machine learning has become so popular that companies are scrambling for talent. Because of this, machine learning is also among the more lucrative fields in the software industry. The current average annual salary for machine learning engineers is $153,151. That’s a lot higher than the average, and those numbers will only go up in the future as the demand for machine learning experts is expected to continue increasing.
What Are Some Other Differences Between Data Mining and Machine Learning?

Let’s sum up what sets data mining and machine learning apart along a few different parameters.
Goal
The goal of machine learning methods is to enable computing systems to learn from training datasets and identify hidden patterns in them. Essentially, the aim is to make pattern analysis and machine intelligence a reality.
Data mining is the process of acquiring and preparing data for the data analysis process. Tools such as a mining algorithm and mining engine are selected based on the objectives of the overall project.
Manual vs. Automatic Process
Data mining is a more manual process than machine learning. This is because it’s not easy to automate the parts that involve finding data sources, cleaning data, and structuring it before analysis.
Machine learning is entirely geared toward automation. The whole goal of the discipline is to automate tasks so that computers are able to learn more and more from training datasets and carry out decision analysis on their own.
Existing Dataset vs. Trained Dataset
Data mining is carried out on an existing dataset. There is no notion of training a dataset in data mining. Machine learning, on the other hand, involves training machine learning algorithms on datasets. This is how they’re able to identify patterns and unearth insights from new datasets.
What Are the Similarities Between Data Mining and Machine Learning?
Although the two fields are quite unlike each other in many ways, there are some similarities. The thing that unites these two fields is their focus on data. Both data mining and machine learning fall under the purview of data science. You need to understand the foundational principles of data science if you want to work with either of them.
Another thing they have in common is the volume of data that is involved in each of them. Data mining and machine learning both usually involve working with large volumes of data. So you need to have systems that can handle these large volumes and process them efficiently.
Data Mining vs. Machine Learning FAQs
We’ve got the answers to your most frequently asked questions:
Is Data Mining a Part of Machine Learning?
No, data mining is not considered a part of machine learning. Data mining is the independent process of preparing and analyzing data to solve a business problem. Machine learning, on the other hand, is the field that concerns itself with teaching computers to learn from trained datasets.
Does Data Mining Require Coding?
Which Career Is Right for Me: Data Mining or Machine Learning?
Machine learning is the right career for you if you have a strong understanding of the computational aspects of the field as well as mathematical concepts like statistics and linear algebra. Data mining is a good choice if you want to focus more narrowly on preparing and processing data for analysis.
Which Career Earns More: Data Mining or Machine Learning?
Machine learning engineers make $153,151 per year on average. Meanwhile, the average salary in the data mining field annually is $96,535.
Since you’re here…
Curious about a career in data science? Experiment with our free data science learning path, or join our Data Science Bootcamp, where you’ll get your tuition back if you don’t land a job after graduating. We’re confident because our courses work – check out our student success stories to get inspired.






